IVF in Iran
Hayat MedTour is a medical tourism facilitator in Iran that has specialized in providing fertility assistance, infertility treatment and IVF in Iran at the best quality and affordable prices
Wednesday, April 27, 2022
HayatMedTour | Fertility Treatment in Iran | IVF in Iran
Boost Male Fertility and Increase Sperm Count
What Helps With Sperm Count and Quality?
If you’ve been trying to have a baby and it’s just not happening, you might have a low sperm count. But don’t panic. It’s actually one of the most common causes of male infertility.
You’ll have to see your doctor to be sure. But there may be things you can do to boost your count naturally. And they’re actually pretty simple.
What Is Low Sperm?
A “normal” sperm count is at least 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen. If you have less than that, you have what doctors consider “low” sperm count, called oligospermia.
When you don’t have enough sperm, there’s less of a chance they’ll reach and fertilize the egg, which can lead to fertility problems.
What Is Quality Sperm?
Even if you have a normal sperm count, they still have to be healthy enough to make the journey from your partner’s vagina to the cervix and uterus to the fallopian tubes. If they’re not, you’ll have a hard time getting them pregnant.
There are three ways your doctor can tell whether your sperm is healthy or “quality.”
Quantity. This measures how many sperm you have in your semen when you ejaculate. Remember, you need at least 15 million sperm per milliliter of semen to have a “normal” sperm count.
Movement. Doctors call this “motility.” It measures how fast or well your sperm move to their final destination -- your partner’s egg. You want at least 50% of your sperm moving.
Structure. Normal sperm have egg-shaped heads and long tails. Sperm use these tails to “swim” to the egg. The more normal-shaped sperm you have, the easier it will be for them to reach your partner’s egg.
Causes of Low Sperm
Any number of things can lead to low sperm count, including previous medical problems, age, and your environment. Your lifestyle factors are
in, too, so if you smoke or use recreational drugs, they can affect your fertility.
How Can I Help My Sperm?
Fortunately, there could be a number of things you can do to increase the amount of healthy, quality sperm your body makes.
Exercise. We know that moderate exercise can boost your mood. But it turns out that it can boost your sperm count, too. Researchers found that men who exercise at least three times per week for 1 hour showed increases in their sperm count and the number of moving sperm, as well.
Stop stressing. It’s easier than it sounds, but do it, especially if you’re trying to have a baby. In a study of 950 men, researchers found that males who had more than two stressful events before starting treatment for infertility were more likely to have low sperm count and motility.
If you smoke, quit. Men who smoke are more likely to have lower sperm count, density, and motility. They also produce less semen than men who don’t smoke.
Say no to drugs. Certain ones, like cocaine and heroin, can affect your ability to get or keep an erection. Other drugs, like marijuana, can make it hard for you to produce sperm. They can also reduce your sperm’s motility or prevent them from developing normally.
Eat right. Choosing a diet of fresh fruits and vegetables may boost your semen quality. Eating fewer fatty foods and a little less protein could also help.
Friday, March 18, 2022
What is azoospermia
Azoospermia means there’s no sperm in a man’s ejaculate. Its causes include a blockage along the reproductive tract, hormonal problems, ejaculation problems, or issues with testicular structure or function. Many causes are treatable and fertility can be restored. For other cases, it may be possible to retrieve live sperm to be used in assisted reproductive techniques.
What is azoospermia?
Azoospermia is a condition in which there’s no measurable sperm in a man’s ejaculate (semen). Azoospermia leads to male infertility.
Are there different types of azoospermia?
There are two main types of azoospermia:
Obstructive azoospermia: This type of azoospermia means that there is a blockage or missing connection in the epididymis, vas deferens, or elsewhere along your reproductive tract. You are producing sperm but it’s getting blocked from the exit so there’s no measurable amount of sperm in your semen.
Nonobstructive azoospermia: This type of azoospermia means you have poor or no sperm production due to defects in the structure or function of the testicles or other causes.
What are the causes of azoospermia?
The causes of azoospermia relate directly to the types of azoospermia. In other words, causes can be due to an obstruction or nonobstructive sources.
Obstructions that result in azoospermia most commonly occur in the vas deferens, the epididymis, or ejaculatory ducts. Problems that can cause blockages in these areas to include:
- Trauma or injury to these areas.
- Infections.
- Inflammation.
- Previous surgeries in the pelvic area.
- Development of a cyst.
- Vasectomy (planned permanent contraceptive procedure in which the vas deferens are cut or clamped to prevent the flow of sperm).
- Cystic fibrosis gene mutation, causes either the vas deferens not to form or causes abnormal development such that semen gets blocked by a buildup of thick secretions in the vas deferens.
Nonobstructive causes of azoospermia include:
- Genetic causes. Certain genetic mutations can result in infertility, including:
- Kallmann syndrome: A genetic (inherited) disorder carried on the X chromosome that if left untreated can result in infertility.
- Klinefelter’s syndrome: A male carries an extra X chromosome (making his chromosomal makeup XXY instead of XY). The result is often infertility, along with a lack of sexual or physical maturity, and learning difficulties.
- Y chromosome deletion: Critical sections of genes on the Y chromosome (the male chromosome) that are responsible for sperm production are missing, resulting in infertility.
- Hormone imbalances/endocrine disorders, including hypogonadotropic hypogonadism. hyperprolactinemia and androgen resistance.
- Ejaculation problems such as retrograde ejaculation where the semen goes into the bladder
- Testicular causes include:
- Anorchia (absence of the testicles).
- Cryptorchidism (testicles have not dropped into the scrotum).
- Sertoli cell-only syndrome (testicles fail to produce living sperm cells).
- Spermatogenic arrest (testicles fail to produce fully mature sperm cells).
- Mumps orchitis (inflamed testicles caused by mumps in late puberty).
- Testicular torsion.
- Tumors.
- Reactions to certain medications that harm sperm production.
- Radiation treatments.
- Diseases such as diabetes, cirrhosis, or kidney failure.
- Varicocele (veins coming from the testicle are dilated or widened impeding sperm production).
How is azoospermia diagnosed?
Azoospermia is diagnosed when, on two separate occasions, your sperm sample reveals no sperm when examined under a high-powered microscope following a spin in a centrifuge. A centrifuge is a laboratory instrument that spins a test sample at a high speed to separate it into its various parts. In the case of centrifuged seminal fluid, if sperm cells are present, they separate from the fluid around them and can be viewed under a microscope.
As part of the diagnosis, your healthcare provider will take your medical history, including asking you about the following:
- Fertility success or failure in the past (your ability to have children).
- Childhood illnesses.
- Injuries or surgeries in the pelvic area (these could cause duct blockage or poor blood supply to the testicles).
- Urinary or reproductive tract infections.
- History of sexually transmitted diseases.
- Exposure to radiation or chemotherapy.
- Your current and past medications.
- Any abuse of alcohol, marijuana, or other drugs.
- Recent fevers or exposure to heat, including frequent saunas or steam baths (heat kills sperm cells).
- Family history of birth defects, learning disabilities, reproductive failure, or cystic fibrosis.
Your healthcare provider will also conduct a physical examination, and will check:
- Your entire body in terms of signs of/lack of maturation of your body and reproductive organs.
- Your penis and scrotum, checking for the presence of your vas deferens, tenderness or swelling of your epididymis, size of the testicles, the presence or absence of a varicocele, and any blockage of the ejaculatory duct (via exam through the rectum) as evidenced by enlarged seminal vesicles.
- Your healthcare provider may also order the following tests:
- Measurement of testosterone and follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels.
- Genetic testing.
- X-rays or ultrasound of the reproductive organs to see if there are any problems with the shape and size, and to see if there are tumors, blockages, or an inadequate blood supply.
- Imaging of the brain to identify disorders of the hypothalamus or pituitary gland.
- Biopsy (tissue sampling) of the testes. A normal biopsy would mean a blockage is probable at some point in the sperm transport system. Sometimes, any sperm found in the testes is frozen for future analysis or can be used in assisted pregnancy.
How is azoospermia treated?
Treatment of azoospermia depends on the cause. Genetic testing and counseling are often an important part of understanding and treating azoospermia. Treatment approaches include:
- If a blockage is the cause of your azoospermia, surgery can unblock tubes or reconstruct and connect abnormal or never developed tubes.
- If low hormone production is the main cause, you may be given hormone treatments. Hormones include follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH), human chorionic gonadotropin (HCG), clomiphene, anastrozole, and letrozole.
- If a varicocele is the cause of poor sperm production, the problem veins can be tied off in a surgical procedure, keeping surrounding structures preserved.
- Sperm can be retrieved directly from the testicle with an extensive biopsy in some men
- If living sperm are present, they can be retrieved from the testes, epididymis, or vas deferens for assisted pregnancy procedures such as in vitro fertilization or intracytoplasmic sperm injection (the injection of one sperm into one egg). If the cause of azoospermia is thought to be something that could be passed on to children, your healthcare provider may recommend genetic analysis of your sperm before assisted fertilization procedures are considered.
Azoospermia
Sunday, February 6, 2022
Infertility Treatment Methods
Infertility Treatment Methods (IVF | ICSI | EGG
Donation)

Tehran (ISNA) - Normal pregnancy depends on various factors and conditions, in case of any disorder in any of them, the chance of fertility is decreased or even may go to zero. Infertility is one of the unwanted life phenomena that have been recently increased. A couple who couldn’t have a baby after a year of having sex without contraception, they are considered as infertile. All things needed couples know about fertility treatment is described in this post.
Infertility and its affecting factors
A couple is considered infertile if they cannot become pregnant after 12 months of unprotected intercourse. For women over the age of 35, infertility means not having fertility after 6 months of unprotected sex. Various causes can lead to infertility in couples. In general, these factors can be summarized in female and male factors.
Female-infertility factors include abnormalities in the female reproductive system or poor egg quality that impairs fertility.
Male-Infertility Cause is one-third of couples’ infertility causes. These types of infertility indicate the presence of dysfunction in sperm production or ejaculation in the male.
Research shows that in a third of cases, a combination of female and male factors causes infertility in couples. About 10% of couples also suffer from unknown causes of infertility.
Different methods of fertility treatment
There are different methods of infertility treatment like IVF, ICSI, IUI, and Egg Donation which can help infertile couples and give them a chance to have a baby. Iran is one of the leading countries in the region and in the world in the field of infertility treatment, therefore many couples choose fertility treatment in Iran for infertility treatment.
Several advanced research institutes and hospitals, provide infertility treatment services like IVF in Iran to both local and international patients. Moreover, other fertility services such as Gender Selection are offered in these centers as well for people who choose fertility treatment in Iran.
In the following, some of the most important methods of infertility treatment are introduced.
What is IVF?
In Vitro Fertilization (IVF) is one of the assisted reproductive techniques (ART) in which a man’s sperm and the woman’s egg are combined in a laboratory dish, where fertilization occurs. When the egg is fertilized, the primary cell begins to divide and form the embryo. The resulting embryo or embryos is/are then transferred to the woman’s uterus to implant and develop naturally.
How is IVF done?
IVF is a common procedure, used to overcome a range of fertility issues. It is a multi-step process involving ovulation induction, egg retrieval, Collection and preparation of sperm, fertilization, culture, and embryo transfer. The IVF process can be explained in these five steps:
• Ovulation induction
The greater the number of oocytes prepared during a treatment cycle, the greater the chance of a healthy fetus forming and subsequently the chance of pregnancy. A doctor prescribes ovulation induction drugs to stimulate the growth of several oocytes in a woman’s cycle.

• Ovum Pick up:
During a minor surgery, the infertile doctor picks up the mature oocytes using a special needle. This is done under conditions of local or general anesthesia. The procedure usually takes less than 30 minutes.
• Collection and preparation of sperm
In vitro fertilization of the oocyte with sperm requires the collection of semen. If the male is unable to produce semen, TESE or PESA methods are used to collect sperm.
The collected sperms are washed by a specific method and examined for motility and shape. Finally, high-quality sperms are selected to fertilize the oocytes.
• Fertilization and embryo culture:
After the ovum picks up, the embryologist examines the obtained egg to select mature eggs that are suitable for fertilization.
The mature eggs are placed in a culture medium and the sperm is transferred to an incubator for fertilization. In IVF, high-motility sperms move to the eggs and fertilize them. Once this occurs, the fertilized eggs are considered embryos.
In conditions with a low number and low quality of sperm, the specialist uses intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI). It is an additional part of an IVF treatment cycle in which a single sperm is injected into each egg to assist fertilization.
• Embryo Transfer
Finally, the selected embryos are prepared for transfer to the uterus. A specialist physician inserts the embryo into the mother’s uterus during a minor surgery without the need for anesthesia.
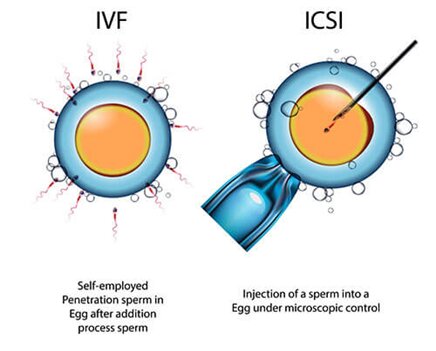
What is the difference between ICSI and IVF?
The difference between IVF and ICSI is in how the oocyte is fertilized. In IVF, the oocyte is exposed to sperm in an in -vitro container until the highly motile sperm enters the oocyte and fertilizes it. But in the ICSI technique, a selected sperm is injected directly into the oocyte through a special needle. In this method, high-quality and motile sperm are separated and ready for injection in a laboratory using a special method. The ICSI method is mostly used in cases where the quality of male sperm is low.
Egg donation
Infertility is not always cured by prescribing medication or using advanced methods of infertility treatment. In cases where a woman’s ovarian reserves are low or the quality of eggs is low, but the uterus and other reproductive organs are healthy, the only fertility way is to receive an egg donated by a volunteer. For a consult of our doctors and specialists and to use the service of Egg Donation in Iran, you can contact us through the HayatMedTour website.
Fertility treatment in Iran
With over 30 years of experience in infertility research and treatment, Iran is one of the world’s pioneers in effective infertility treatment. There are more than 80 specialized fertility treatment centers in Tehran, Urmia, Yazd, Isfahan, and other cities of Iran. These clinics with the up-date of knowledge and equipment in the world; offer various methods for infertility treatments with the best quality and reasonable prices.
The high quality and affordable cost of fertility treatments in Iran have led many medical tourists to choose this destination for the treatment of their infertility problems.
End Item
Wednesday, January 19, 2022
How to Improve Sperm Quality
If you and your partner are planning a pregnancy, you might be wondering about the health of your sperm. Understand the factors that can affect male fertility — then consider steps to help your sperm achieve your goal.
What determines sperm health?
Male reproductive system
Sperm health depends on various factors, including quantity, movement, and structure:
- Quantity. You're most likely to be fertile if your ejaculate — the semen discharged in a single ejaculation — contains at least 15 million sperm per milliliter. Too little sperm in an ejaculation might make it more difficult to get pregnant because there are fewer candidates available to fertilize the egg.
- Movement. To reach and fertilize an egg, sperm must move — wriggling and swimming through a woman's cervix, uterus, and fallopian tubes. This is known as motility. You're most likely to be fertile if at least 40% of your sperm are moving.
- Structure (morphology). Normal sperm have oval heads and long tails, which work together to propel them. While not as important a factor as sperm quantity or movement, the more sperm you have with a normal shape and structure, the more likely you are to be fertile.
What causes male fertility problems?
Various medical issues can contribute to male fertility problems, including:
- A problem in the hypothalamus or the pituitary gland — parts of the brain that signal the testicles to produce testosterone and sperm (secondary hypogonadism)
- Testicular disease
- Sperm transport disorders
Age can also play a role. The ability of sperm to move and the proportion of normal sperm tend to decrease with age, affecting fertility, especially after age 50.
What's the best way to produce healthy sperm?
You can take simple steps to increase your chances of producing healthy sperm. For example:
- Maintain a healthy weight. Some research suggests that increasing body mass index (BMI) is linked with decreasing sperm count and sperm movement.
- Eat a healthy diet. Choose plenty of fruits and vegetables, which are rich in antioxidants — and might help improve sperm health.
- Prevent sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Sexually transmitted infections — such as chlamydia and gonorrhea — can cause infertility in men. To protect yourself, limit your number of sexual partners and use a condom each time you have sex — or stay in a mutually monogamous relationship with a partner who isn't infected.
- Manage stress. Stress can decrease sexual function and interfere with the hormones needed to produce sperm.
- Get moving. Moderate physical activity can increase levels of powerful antioxidant enzymes, which can help protect sperm.
What's off-limits?
Sperm can be especially vulnerable to environmental factors, such as exposure to excessive heat or toxic chemicals. To protect your fertility:
- Don't smoke. Men who smoke cigarettes are more likely to have low sperm counts. If you smoke, ask your doctor to help you quit.
- Limit alcohol. Heavy drinking can lead to reduced testosterone production, impotence, and decreased sperm production. If you drink alcohol, do so in moderation.
- Avoid lubricants during sex. While further research is needed on the effects of lubricants on fertility, consider avoiding lubricants during intercourse. If necessary, consider using baby oil, canola oil, egg white, or a fertility-friendly lubricant, such as Pre-Seed.
- Talk to your doctor about medications. Calcium channel blockers, tricyclic antidepressants, anti-androgens, and other medications can contribute to fertility issues. Anabolic steroids can have the same effect.
- Watch out for toxins. Exposure to pesticides, lead and other toxins can affect sperm quantity and quality. If you must work with toxins, do so safely. For example, wear protective clothing and equipment, and avoid skin contact with chemicals.
- Stay cool. Increased scrotal temperature can hamper sperm production. Although the benefits have not been fully proved, wearing loose-fitting underwear, reducing sitting, avoiding saunas and hot tubs, and limiting scrotum exposure to warm objects, such as a laptop, might enhance sperm quality.
Chemotherapy and radiation therapy for cancer can impair sperm production and cause infertility that might be permanent. Ask your doctor about the possibility of retrieving and storing sperm before treatment.
When is it time to seek help?
Adopting healthy lifestyle practices to promote your fertility — and avoiding things that can damage it — can improve your chances of conceiving. If you and your partner haven't gotten pregnant after a year of unprotected sex, however, you might consider being evaluated for infertility. A fertility specialist also might be able to identify the cause of the problem and provide treatments that place you and your partner on the road to parenthood.
Monday, December 6, 2021
How to improve egg quality for pregnancy
How to Improve Egg Quality
Having healthy eggs is one of the most important and influential factors on a woman's fertility. Therefore, ensuring the health and quality of eggs before pregnancy is very important. Most women who have weak oocytes are unable to conceive normally and will inevitably have to use infertility treatments such as IVF. In some cases, the quality of the eggs is so low that the only way to get pregnant is to use Egg Donation. Therefore, strengthening the eggs and finding ways to increase their quality is one of the most important concerns before attempting to conceive.
The effect of age on the egg quality

In the past, it was believed that every woman was born with all her ovarian reserves and could not produce more eggs after birth. Therefore, age was the most important factor affecting the health and quality of eggs and with increasing age, the quality and quantity of eggs decreases. But new scientific findings show that stem cells in the ovaries can produce new eggs during the reproductive years. However, it should be noted that age still has an important effect on the process of ovulation and the production of new egg cells, because the production of new oocytes is possible only at the reproductive age, and with increasing age, the possibility of embryo implantation in the uterus decreases.
Although it is not possible to prevent a decrease in fertility and ovulation with aging, there are ways to improve the egg quality and increase the chances of pregnancy at an older age. Factors such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, lifestyle changes and the use of supplements, etc. can have a positive effect on the quality of eggs. Therefore, observing these items is very important to increase the quality of eggs before attempting to conceive, especially at the age of over 40 years.
Factors affecting the quality of egg
The quality of the eggs largely depends on the environment in which the ovary grows. Oocytes usually go through a 90-day period from the beginning of development until they reach puberty and are released from the ovaries. . Therefore, the ovarian environment during these 90 days has a great impact on the quality of the released eggs. In general, women over the age of 40 have a poor ovarian environment to grow quality oocytes. However, following some tips for 3 to 4 months before getting pregnant can help them to increase the quality of eggs and pregnancy health. The most important factors affecting the health and quality of eggs are:
Proper diet
We know that proper diet and nutrition have a direct impact on our health. So it is not surprising that diet may affect the reproductive health and quality of eggs. Women who are planning to become pregnant should eat foods that are high in vitamin A, such as liver, fish, and a variety of high-fat dairy products, to improve the quality of their eggs. Adequate intake of vitamin A by the body contributes to the proper response of the ovaries, increasing the quality of eggs and fetal growth. In addition, research shows that eating omega-3 foods such as fish and flaxseed is effective in maintaining fertility and improving egg quality.

Doctors recommend a low-carb, high-fat diet (unsaturated fat) before pregnancy. This diet helps to improve the quality of eggs in two ways, one is to reduce inflammation and the other is to balance reproductive hormones. Inflammation can cause tissue damage, reduce blood flow to the ovaries, and interfere with the ovaries' ability to receive nutrients. However, adequate ovarian nutrition and adequate blood flow are essential to ensure the growth of eggs and the production of quality eggs. Therefore, to reduce inflammation, it is recommended to limit carbohydrate intake because the breakdown of carbohydrates in the body causes the production of glucose, fructose, and other sugars that cause inflammation.
The balanced production of reproductive hormones is another factor affecting the quality of eggs. When hormones become unbalanced in the body (a common symptom of polycystic ovary syndrome; PCOS), the ovaries do not function properly and the eggs mature at low speed and quality.
Therefore, to increase the quality of eggs, it is recommended to increase the consumption of unsaturated fats because fat gives energy to the body and helps in the production of hormones and the growth of egg cells. In addition, it is recommended to avoid excessive caffeine consumption because the caffeine in various ways impairs women's reproductive function.
Lifestyle
Some simple lifestyle changes can improve egg quality and increase your chances of getting pregnant. Some of these changes are:
No.1 Having enough sleep
Adequate and quality sleep is an important part of a healthy lifestyle. During sleep, the body repairs cells and recovers lost energy. In addition, during sleep, the hormones needed for reproduction are released. Therefore, adequate sleep contributes greatly to the growth and health of the eggs. The brain secretes the hormone melatonin to improve sleep. In addition to improving sleep quality, this hormone also increases egg quality and facilitates ovulation and fetal growth. With age, the level of the hormone melatonin decreases, so in women over 40, it is important to choose methods to improve sleep. Eating a healthy diet, managing stress, and reducing cell phone and TV use can help improve sleep patterns.
No.2 Avoiding alcohol and smoking
Research shows that alcohol consumption and smoking reduce the quality of eggs and increase the number of abnormal eggs. The chemicals in cigarettes cause the DNA of the egg to mutate, which is usually not suitable for fertility. Therefore, avoiding alcohol and smoking has a significant effect on egg health and quality.
No.3 Stress management
Stress causes imbalance and causes many problems in the body. When we are stressed, the body begins to produce the hormones cortisol and prolactin. These hormones can disrupt the ovulation process and prevent the production of quality eggs. The importance of stress management in the infertility treatment process is twofold. Because fertility treatment itself is a stressful process and if this stress is managed properly, it will have a great impact on the success of treatment.

No.4 Exercising
Light exercise such as walking and yoga are great ways to reduce stress, increase blood flow to the genitals and strengthen the immune system. As mentioned earlier, the ovaries need enough blood flow to provide nutrients and oxygen in order to be a good environment for quality eggs to grow. Therefore, exercising helps a lot to increase blood flow and increase the quality of eggs. In addition, drinking at least 8 glasses of water a day and doing abdominal massages increase blood circulation in the ovaries and uterus and improve the quality of eggs.
Use of supplements
Using supplements is one of the best options to complete a healthy diet and ensure the health of the body and reproductive health. Supplements can help improve egg quality in women of childbearing age and over 40 years. Research shows that the nutrients and vitamins in supplements increase the ability of the egg to divide and improve the quality of the formed fetus. In addition, the antioxidants in supplements prepare the ovarian environment to improve egg quality.
The most important supplements recommended to improve egg quality in women over 40 are:
Omega-3: Omega-3 helps maintain fertility in women and improves egg quality by delaying ovarian aging. Getting enough omega-3 through your diet is difficult, so it is recommended to take a fish oil supplement that contains adequate amounts of omega-3.
Coenzyme Q10: Coenzyme Q10 (Co Q10) is an antioxidant that enhances the ability of an egg to divide. The level of this enzyme in the body decreases with age. Therefore, supplementation of this enzyme is recommended to improve the quality of eggs and provide the energy needed for egg DNA amplification in women over 40 years of age.
Vitamin A: Vitamin A plays an important role in improving egg quality and fetal growth. Vitamin A supplementation helps women over the age of 40 to ensure proper egg growth.
Other Supplements: Supplements containing vitamin E, zinc, folate, and some B vitamins can also help increase egg quality.
The effect of increasing egg quality on the success of fertility treatments
Paying attention to strategies to improve egg quality is important not only for women who are planning to become pregnant at an older age, but also helps women who intend to use fertility treatments such as IUI, IVF, and ICSI and increases the chances of successful treatment.
Infertility treatments using high-quality eggs increase the likelihood of embryo formation. In addition, embryos formed with quality eggs have a better chance of implanting in the uterus and will continue to have more successful cell division.
Friday, November 5, 2021
Male fertility testing
Diagnostic Tests for Male Infertility
Many infertile couples have more than one cause of infertility, so it's likely you will both need to see a doctor. It might take a number of tests to determine the cause of infertility. In some cases, a cause is never identified.
Infertility tests can be expensive and might not be covered by insurance — find out what your medical plan covers ahead of time.
Diagnosing male infertility problems usually involves:
- General physical examination and medical history. This includes examining your genitals and asking questions about any inherited conditions, chronic health problems, illnesses, injuries, or surgeries that could affect fertility. Your doctor might also ask about your sexual habits and about your sexual development during puberty.
- Semen analysis. Semen samples can be obtained in a couple of different ways. You can provide a sample by masturbating and ejaculating into a special container at the doctor's office. Because of religious or cultural beliefs, some men prefer an alternative method of semen collection. In such cases, semen can be collected by using a special condom during intercourse.
Your semen is then sent to a laboratory to measure the number of sperm present and look for any abnormalities in the shape (morphology) and movement (motility) of the sperm. The lab will also check your semen for signs of problems such as infections.
Often sperm counts fluctuate significantly from one specimen to the next. In most cases, several semen analysis tests are done over a period of time to ensure accurate results. If your sperm analysis is normal, your doctor will likely recommend thorough testing of your female partner before conducting any more male infertility tests.
Your doctor might recommend additional tests to help identify the cause of your infertility. These can include:
- Scrotal ultrasound. This test uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images inside your body. A scrotal ultrasound can help your doctor see if there is a varicocele or other problems in the testicles and supporting structures.
- Transrectal ultrasound. A small, lubricated wand is inserted into your rectum. It allows your doctor to check your prostate and look for blockages of the tubes that carry semen.
- Hormone testing. Hormones produced by the pituitary gland, hypothalamus, and testicles play a key role in sexual development and sperm production. Abnormalities in other hormonal or organ systems might also contribute to infertility. A blood test measures the level of testosterone and other hormones.
- Post-ejaculation urinalysis. Sperm in your urine can indicate your sperm are traveling backward into the bladder instead of out your penis during ejaculation (retrograde ejaculation).
- Genetic tests. When sperm concentration is extremely low, there could be a genetic cause. A blood test can reveal whether there are subtle changes in the Y chromosome — signs of a genetic abnormality. Genetic testing might be ordered to diagnose various congenital or inherited syndromes.
- Testicular biopsy. This test involves removing samples from the testicle with a needle. If the results of the testicular biopsy show that sperm production is normal your problem is likely caused by a blockage or another problem with sperm transport.
- Specialized sperm function tests. A number of tests can be used to check how well your sperm survive after ejaculation, how well they can penetrate an egg, and whether there's any problem attaching to the egg. These tests aren't often used and usually don't significantly change recommendations for treatment.
Monday, October 25, 2021
Fertility Treatment
There are 3 main types of fertility treatment:
- medicines
- surgical procedures
- assisted conception – including intrauterine insemination (IUI) and in vitro fertilizations (IVF)
Medicines
Common fertility medicines include:
- clomiphene – encourages the monthly release of an egg (ovulation) in women who do not ovulate regularly or cannot ovulate at all
- tamoxifen – an alternative to clomiphene that may be offered if you have ovulation problems
- metformin – is particularly beneficial for women who have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- gonadotrophins – can help stimulate ovulation in women, and may also improve fertility in men
- gonadotrophin-releasing hormone and dopamine agonists – other types of medicine prescribed to encourage ovulation in women
Some of these medicines may cause side effects, such as nausea, vomiting, headaches and hot flushes.
Speak to your doctor for more information about the possible side effects of specific medicines.
Medicine that stimulates the ovaries is not recommended for women with unexplained infertility because it has not been found to increase their chances of getting pregnant.
Surgical procedures
There are several types of surgical procedures that may be used to investigate fertility problems and help with fertility.
Fallopian tube surgery
If your fallopian tubes have become blocked or scarred, you may need surgery to repair them.
Surgery can be used to break up the scar tissue in your fallopian tubes, making it easier for eggs to pass through them.
The success of surgery will depend on the extent of the damage to your fallopian tubes.
Possible complications from tubal surgery include an ectopic pregnancy, which is when the fertilised egg implants outside the womb.
Endometriosis, fibroids and PCOS
Endometriosis is when parts of the womb lining start growing outside the womb.
Laparoscopic surgery is often used to treat endometriosis by destroying or removing fluid-filled sacs called cysts.
It may also be used to remove submucosal fibroids, which are small growths in the womb.
If you have polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), a minor surgical procedure called laparoscopic ovarian drilling can be used if ovulation medicine has not worked.
This involves using either heat or a laser to destroy part of the ovary.
Read more about laparoscopy.
Correcting an epidydimal blockage and surgery to retrieve sperm
The epididymis is a coil-like structure in the testicles that helps store and transport sperm.
Sometimes the epididymis becomes blocked, preventing sperm from being ejaculated normally. If this is causing infertility, surgery can be used to correct the blockage.
Surgical extraction of sperm may be an option if you:
- have an obstruction that prevents the release of sperm
- were born without the tube that drains the sperm from the testicle (vas deferens)
- have had a vasectomy or a failed vasectomy reversal
Both operations take a few hours and are done under local anesthetic as outpatient procedures.
You'll be advised on the same day about the quality of the tissue or sperm collected.
Any sperm will be frozen and placed in storage for use at a later stage.
Assisted conception
Intrauterine insemination (IUI)
Intrauterine insemination (IUI), also known as artificial insemination, involves inserting sperm into the womb via a thin plastic tube passed through the cervix.
Sperm is first collected and washed in a fluid. The best quality specimens (the fastest moving) are selected.
Read more about IUI.
In vitro fertilizations (IVF)
In vitro fertilizations (IVF), is when an egg is fertilized outside the body. Fertility medicine is taken to encourage the ovaries to produce more eggs than usual.
Eggs are removed from the ovaries and fertilized with sperm in a laboratory. A fertilized egg (embryo) is then returned to the womb to grow and develop.
Egg and sperm donation
If you or your partner has an infertility problem, you may be able to receive eggs or sperm from a donor to help you conceive. Treatment with donor eggs is usually done using IVF.
Thursday, October 7, 2021
Ways to improve egg quality
ways to improve egg quality before pregnancy or IVF
DHEA Supplements
– Dehydro-epiandrosterone or DHEA is a mild, well-tolerated, male hormone that can have remarkable results for women with diminished ovarian reserve.Very low levels of androgens in the ovaries may result in reduced ovarian reserve and poor-quality eggs, which can be turned around to a small extent with the supplementation of DHEA, as several trials have proven.
The supplements can be taken as an oral dosage of 75mg-100mg (strictly after consultation with your doctor), for a period of at least 2 months before ovum pick-up is done. The actual effect is known to peak in 4-5 months.
Side effects, although rare, can be caused by the androgynous nature of DHEA. Some women may see acne, hair loss, abnormal growth of facial hair, etc. but even these tend to reverse as your hormones return to normal levels.
CoQ10 supplements
– CoQ10 (Coenzyme Q10) is an antioxidant that helps improve the quality of eggs. It acts as a nutrient for the mitochondria, which is the energy-house of human cells.As you age, the number of healthy mitochondria and levels of CoQ10 decline. CoQ10 supplements can boost the energy in your egg cells.
A Chinese study involving 169 women, found that the participants who were given CoQ10 supplements had a higher number of eggs retrieved, better fertilization rates, better embryo quality, and hence, better chances of a successful pregnancy.Glutathione
– Another powerful antioxidant that fights free radicals and reduces the oxidative stress on your egg cells, resulting in healthier eggs and consequently, better embryos.L-arginine –
By helping improve the blood supply to the uterus and ovaries, L-arginine helps create a better environment for egg production and fertilization.Myo-Inositol
– PCOS often results in fertility problems as it causes the release of immature eggs, which cannot be fertilized well. Inositol supplements, especially when combined with Folic Acid, may improve your PCOS by reducing the level of triglycerides in the blood and improving ovarian function.As the insulin function improves the symptoms of PCOS get better and it may further help by promoting ovulation.
Administration of inositol and folic acid in anovulatory women, taken daily for 3 months, was found to induce ovulation in 62% of the women in this study.
Nutrition
– British researchers have found that female egg quality is affected by having too many refined carbohydrates, which break down quickly and cause a sudden spike in blood sugar.So, avoid excessive bread, pasta, processed foods, and sugar-rich foods.
It is recommended that you have a balanced diet that comprises less than 40% carbohydrates, at least 35% protein, and plenty of leafy greens, berries, and fruits that provide vitamins, minerals, and anti-oxidants.
Avoid smoking, caffeine, alcohol
– Nicotine is known to be toxic to your cells, including egg cells. Also, caffeine and alcohol, when consumed in excess can be harmful to your pregnancy.Exercise
– Improving oxygen-rich blood flow to the ovaries can help improve the quality of eggs. Exercising and drinking more water is the simplest way to achieve that.Obesity can compromise mitochondrial function and increase oxidative stress on your cells. Having a normal body mass index (BMI) helps improve your odds of conceiving successfully.
Manage stress
– While stress does not directly cause infertility, it can affect the quality of your eggs, causing them to function less. Prolonged stress also produces hormones such as cortisol and prolactin, which may interfere with normal ovulation.Acupuncture and Yoga
– Acupuncture and yoga can both reduce anxiety and stress, improve blood flow to the ovaries and help your body get rid of toxins—all factors that may, over time, result in improved egg quality and ovarian function.One of our own authors believes that acupuncture helps in conception as it did for her.
Sunday, September 26, 2021
Tips to Prepare for Fertility Treatment
Most Important Tips to Prepare for Fertility Treatment
Over 80% of the time, fertility drugs can stimulate ovulation—fertility treatments are being done now more than ever. Current technology offers fertility treatments to make pregnancy a reality for many couples who would otherwise struggle. Fertility treatments are a highly involved process and can be both emotionally and physically taxing. However, certain things can help you prepare for fertility treatments to alleviate stress and increase the likelihood of a healthy pregnancy.
7 Tips to prepare for fertility treatments
- Quit unhealthy habits - When starting fertility treatments, quit smoking, drinking, and staying up late to help prepare your body for pregnancy while increasing the chances of getting pregnant.
- Maintain a healthy weight - Being overweight can affect pregnancy. Excess weight increases the risk of a miscarriage and can affect outcomes with in vitro fertilization procedures (IVF). A high BMI also affects the safety of undergoing anesthesia or sedation, which is necessary with IVF.
- Eat a balanced diet - Eating a wide variety of fruits, vegetables, lean proteins, and healthy fats can help you maintain a good weight while building up nutrition for better overall health.
- Get quality sleep - Sleep is crucial for cellular repair, maintaining stress levels, and essential for fertility. Set a goal of getting between 7/ 9 hours of quality sleep each night.
- Maintain stress levels- Stress can hurt the chances of successful fertility. Seek ways to maintain stress during this process. Try things like acupuncture, walking, journaling, and meditating to decrease anxiety.
- Change workout routines - Exercise is great for increasing fertility. Replacing running and extreme exercising like bodybuilding to a gentler routine. Yoga, walking, swimming, hiking, and biking are wonderful ways to get gentle exercise during fertility treatments and pregnancy.
- Begin taking a prenatal vitamin - It is recommended to increase nutrients during fertility treatments. Prenatal vitamins are an excellent choice to ensure the body has enough folic acid, which aids in developing the brain and spinal cord during pregnancy. Please discuss with your doctor what prenatal vitamins they recommend.
Monday, September 20, 2021
The Cost of IVF Operation
How Much Does IVF Cost?
In vitro fertilization (IVF) allows couples suffering from infertility to have children of their own. The procedure is relatively common; about 5% of children in America today were conceived through IVF, according to Amy Schutt, M.D., a reproductive endocrinologist at the Family Fertility Center at Texas Children’s Pavilion for Women. But despite its widespread availability, IVF is a pricey prospect, and proper financial planning is key. Here’s everything you need to know about the total cost of undergoing IVF.
The Cost of IVF
The cost of IVF depends on several different factors, like geographic location and egg type (fresh, frozen, or donor). But Dr. Schutt says the typical IVF cost in the United States is $12,000. This includes the procedure (retrieving eggs, inseminating them with sperm, and inserting them into the uterus), as well as ultrasounds, blood tests, embryo storage, anesthesia, and more. Patients also can expect to pay an additional $3,000 - $5,000 for medications that stimulate egg production.
The cost of IVF in some other countries is lower. for example, the cost of IVF in Iran is about 2500 $- 3500$ ( Doctor visits, analyses, ultrasounds, medicines, ICSI, embryo transfer, and freezing the remaining embryos).
What’s more, couples must decide whether they want genetic testing, which screens for chromosomal defects. With this testing, doctors can choose the healthiest embryos of the batch to insert into your uterus. Genetic testing also allows you to see the sex of your baby; some clinics even let you choose the gender. If you opt for genetic testing, know that it can add several thousand dollars to the overall IVF cost.
Here are some other factors that may affect your total bill:
Using Frozen Embryos: If using frozen embryos, whether, from yourself or a donor, you skip one part of the IVF process: retrieving eggs from the ovary with ultrasound imaging and a needle. Because of this, IVF with frozen embryos costs less – usually around $3,000 to $5,000 total. (Keep in mind, however, that you may have already paid for freezing and storing your eggs).
Using Donor Eggs: Usually the procedural cost is lower when using donor eggs because you won’t need to retrieve eggs from the ovaries. However, you’ll spend anywhere from $25,000 - $30,000 on the eggs.
The cost of IVF in some other countries is lower. for example, the cost of egg donation in Iran is about 4000$ ( Doctor visits, analyses, ultrasounds, medicines, donated eggs ICSI, embryo transfer, and freezing the remaining embryos).
Intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI): If a man’s sperm has low mobility, the doctor can insert it directly into the egg with a process called ICSI. This will cost about $1,000 to $2,500.
Surrogacy: With surrogacy, a couple will need to shell out for legal fees and surrogate payment, in addition to the IVF procedure cost. This ranges from $50,000 to $100,000.
It’s important to note that the costs outlined above are for one IVF cycle. The success rate of IVF for those under 35 years old is around 54%, according to a 2015 study by the Society for Assisted Reproductive Technology (SART). The success rate depends on age and types of egg used (fresh, frozen, or donor); for more, check out the complete study here. Given these odds, many patients end up undergoing more than one IVF attempt, thus doubling or tripling the projected price.
Does Insurance Cover IVF?
The high cost of IVF may leave many wondering if the procedure is covered by insurance. The answer isn’t clear-cut. While most insurance companies won’t offer assistance, others may partially or fully cover IVF procedures, infertility diagnoses, or medication. Fifteen states mandate some kind of insurance coverage for fertility treatments: Arkansas, California, Connecticut, Hawaii, Illinois, Louisiana, Maryland, Massachusetts, Montana, New Jersey, New York, Ohio, Rhode Island, Texas, and West Virginia. Check with your insurance provider and workplace for more information about coverage.
You may also consider researching your fertility clinic’s financial plans. Some clinics offer refund plans that let you pay for multiple IVF cycles upfront. If none of the cycles are successful, some amount of refund will be rewarded.